Restaurant robotics is a term that is used to describe the use of technology in restaurants to automate certain tasks. This can include anything from using automats to take orders to use robots to cook food. Some people view restaurant robotics as a way to reduce labor costs, while others see it as a way to improve the customer experience. No matter which side of the argument you fall on, there is no doubt that restaurant robotics is changing the game for both restaurateurs and customers alike and should be considered in all chains’ restaurant strategic planning.
How Robots Are Changing the Restaurant Landscape
Restaurant margins have been under pressure for years. Already in 2019, restaurants were not able to pass inflationary costs on to consumers (back then, the average restaurant price increase was 3.1% while labor cost was growing at 3.8% and food at 5%). And in 2021 restaurant price increases were 4.5% compared to labor costs growing by 8.9%. In addition: $235 billion are paid annually in restaurant wages in the U.S. and the foodservice industry has a $95 billion annual turnover cost.
In this context, some estimates indicate robotics can save between 30% and 70% on labor cost for restaurants. And even though there are only 1 service robots for every 1,500 restaurants (globally, as of 2022), many are coming out of the prototype phase and can do almost anything a human can. Some of the capabilities for monotonous jobs are closer than most people think and penetration is going to happen faster than delivery.
We believe restaurant robotics will soon be as ubiquitous as the POS and commercial dish machine. This is the time to invest.
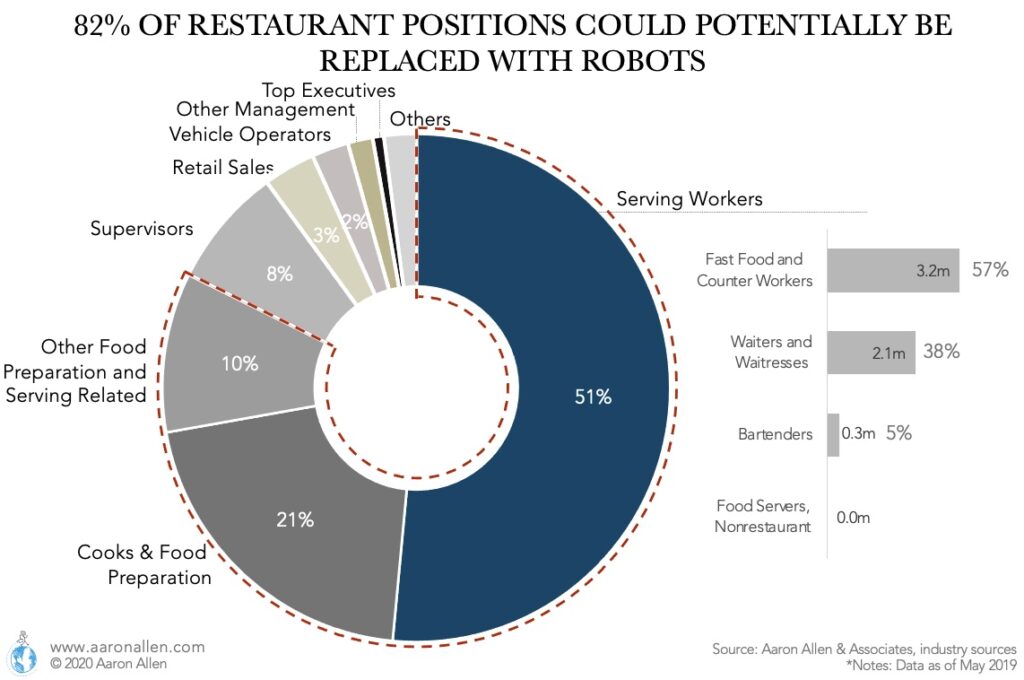
Are robots going to succeed in the restaurant industry? Here are some robotics statistics to think about the answer. And when you think about it, also keep in mind how restaurant CEOs were able to make bold-bets on innovation.
- The restaurant industry is short on workers: there are around 11.7 million workers as of 2022, that’s 300k jobs short compared to 2019 (as of August)
- Estimates put the restaurant turnover rates around 75% — with a cost of $2.2k for hourly employees (or equivalent to $95 billion annually for the U.S. foodservice industry)
- Up to 82% of restaurant positions could, to some extent, be replaced with robots
- According to the NRA, 80% of restaurants are understaffed
- A survey indicated that 90% of restaurants are considering kitchen automation technology (Wakefield Research)
- Some estimates indicate that the cost of robots has declined by 50% over the last three decades (across industries)
- Estimates put the global robot industry in the range $40 billion – $65 billion and projected to double in size over the next seven years
- The cost of implementing robotics is the top challenge to automate
Leading Restaurant Robotics Companies
While the use of robots has tripled in the last decade across industries like electronics, automotive, machinery, and food manufacturing; foodservice has lagged behind.
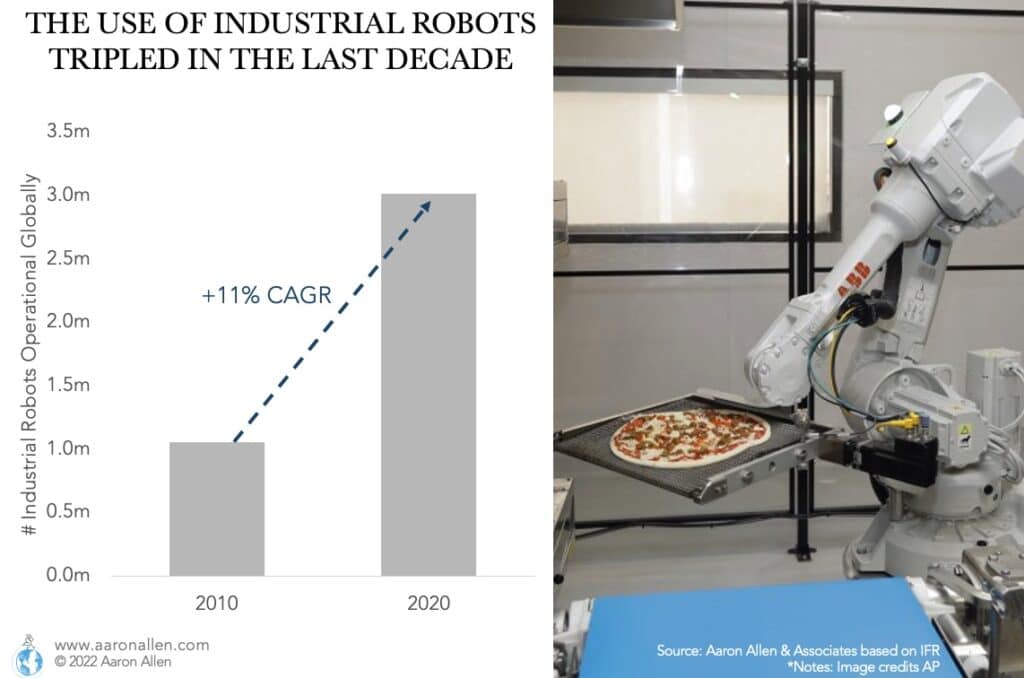
As technology advances, restaurant robots are becoming an increasingly popular option for businesses all sizes. Whether you’re looking to purchase your first robot or are interested in learning more about the benefits of this restaurant technology, this list is a good starting point for the market landscape.
Robotic Arms in Restaurants
Ally Robotics Wants to Make Robots More Affordable
Ally Robotics is a startup trying to make robots affordable and easy to use. Ally has partnered with Miso to supply the robotic arms for Flippy (with $30 million in potential revenue committed, according to the company), with a potential to reduce Flippy’s costs by 30%. The company is raising a series A as of July 2022.
Nala Robotics Competing in Robotic Arms
Nala is a robotic chef able to handle a multitude of cuisines. The AI-based robotic arm has been tested to make pizzas, wings, pasta, bowls, French fries, and more.
Flippy Is One of the Most Popular Restaurant Robots
Pasadena-based robotics company Miso Robotics is behind Flippy, the robotic arm that is shaking up the restaurant industry. Equipped with sensors and artificial intelligence, Flippy can handle fryers and flip burgers – tasks that are traditionally done by human cooks. The result is a faster and more efficient kitchen, with miso claiming that their robot can prep food twice as fast and increase throughput by 30%. The initial cost of Flippy2 starts at $3,000 per month. As of mid-2022, the company has raised more than $50 million from investors, mostly via crowdfunding.
Bartender Robots in Restaurants
Makr Shakr is One of the First Robot Bartenders
Makr Shakr It is a robotic solution for the cocktail industry, based in Turin, and presented in 2013 by google I/O, when the robotic arm had a cost of $110 thousand. The company partnered with Royal Caribbean cruises.
Cecilia.ai is an AI Powered Drinks Vending Machine
Cecilia.ai is a robot for the preparation of cocktails with interactive, conversational AI. Cecilia looks like a vending machine and it’s being used by companies like Microsoft.
Bowls and Salad-Maker Robots in Restaurants
Chowbotics Salad-Maker Robot Sally Was Also Shut Down
Restaurant robots have become increasingly popular in recent years as a way to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency. One of the most famous restaurant robots is Chowbotics’ Sally, a salad-maker robot that costs around $30 thousand. Hospital and university campuses are some of the most common locations for Sally units, as they are available 24 hours a day. However, the company was acquired by Doordash in 2021, and it was announced that operations would be shut down by mid-2022. The last known valuation of the company was $46 million (in 2018).
Spyce Was One of the Pioneers in Restaurant Kitchen Robotics
Spyce was founded in 2015 and acquired by Sweetgreen in 2021. Spyce had an automated restaurant in the Boston area, capable of cooking bowls with minimal employee supervision.
Beastro Was Built as a Dark Kitchen Solution
Beastro automates cooking and can be adapted for any type of dish (including Italian, Asian, soups, salads). The company claims to reduce labor costs by half, and can produce up to 45 dishes per hour. The cost is $7,500 per month — for a restaurant open 8 hours per day at maximum capacity it would translate into 70 cents per dish.
Autec, the Sushi-Making Robot
This company offers four options for sushi-making robots (with a cost of around $14k each) that can sit in the kitchen counter and require minimal training and human interaction.
Food Delivery Robots Are Part of a Fast-Growing Category
Globally, delivery robots are projected to grow at a 30% CAGR. These are some of the most successful food delivery robotic companies.
Starship is the Largest Fleet of Last-Mile Food Delivery Vehicles
Starship Technologies is one of the last-mile delivery startups, operating autonomous delivery vehicles in the U.S. and UK and using machine learning to improve their navigational skills. The company has about 1.7k units in operations (as of 2022) and raised a total of $200 million, with $57 million coming from the European Investment Bank.
Nuro Valued at $8.6 Billion
Nuro food delivery robots drive in the open road and have chill and heated compartments. Nuro autonomous vehicles have been piloted by Domino’s , Chipotle, Kroger, Walmart, 7-Eleven, and FedEx. The robot is call R2 and can drive on public roads in some states. Nuro raised $600 million in 2021 at an $8.6 billion valuation — higher than the market cap of Wendy’s, Shake Shack, and Sweetgreen, combined.
Serve Robotics was Divested from Postmates
Serve Robotics was Postmates last-mile delivery vehicle, founded in 2017 and spun off in 2021. The robot uses Lidar sensors to map and navigate without human intervention. Some of Serve investors are Uber, 7-Eleven, and Delivery Hero’s CVC.
Kiwibot Autonomous Robots to Grow by 6x
Kiwibot was launched in 2017 and has currently a fleet of around 200 robots and mainly operates in campuses. In 2022 the company raised $7.5 million in a Pre-Series A round (bringing the total funding to $14 million) and announced a deal with Sodexo to 6x its fleet.
Alibaba Group Developed Xiaomanlv Robots
Xiaomanlv Robots are driverless vehicles delivering products in China. They have a fleet of 500 autonomous robots and are mainly present at university campuses in China.
Doordash Is Also Investing in Autonomous Vehicles
In June 2022 the food delivery company filed a patent application for a self-driving vehicle with storage for perishable goods. Doordash has announced it intends to automate the middle mile. It’s not the first time the company invests in technology — some previous investments were Scotty Labs acquisition in 2019 and Chowbotics in 2021.
Popular Robot Waiters
BellaBot from Pudu Robotics
In today’s fast-paced world, efficiency is key. That’s why more and more businesses are turning to robots to help with tasks like product delivery. One such robot is the Bellabot, developed by Pudu Robotics. This little robot can deliver up to 400 products a day, making it a valuable asset for busy bars and restaurants. The bellabot costs $17,000 per unit.
Matradee Is a Leading Player in the Restaurant Robot Server Category
Matradee is a restaurant robot server developed by Richtech. It facilitates internal delivery, allowing more interaction between human personnel and customers. The company is located in Austin Texas. Matradee can open kitchen doors and takes food from the kitchen to the table, commanded remotely with a smartwatch.
Servi Robot (Bear Robotics)
Servi is a restaurant robot responsible for serving drinks, food running, and table bussing. It serves as a personal assistant to staff. Some of the restaurant chains using Servi are Chili’s and Denny’s. Bear Robotics closed an $81M Series B funding round in March 2022, led by IMM Investment Corp.
SoftBank Robotics’ Pepper Takes Orders
Pepper is a robot that detects emotions. This robot is part of Softbank’s portfolio. In the coffee shop Pepper Parlor (in Japan), the robot is being used to take orders and entertain guests with games and fortune telling. The robot was also being used in a Scottish grocery store in a guest-facing role but was fired for directing people to the alcohol aisle when they asked for directions.
Japan-Based Smile Robotics ACUR-C Clears Your Table
This robot is under development and can serve and clear dishes from the table with a robotic arm.
Pizza Robots Disrupting the Category
The global pizza industry is worth $160 billion. After delivery disrupted the category a few decades ago (the exact time frame depending on the geography), it’s about to be disrupted again. These are some of the pizza robots that can do so.
Picnic, a Pizza Robot
Picnic is a restaurant that sells pizza which are prepared by a production line that uses robotics and artificial intelligence. It is located in Seattle. The cost ranges between $3,500 and $5,000 per month. In 2021, the Series A raised $20.5 million.
Piestro Automates Pizza Making
Piestro robots make pizza at a lower cost. The company has $580 million in pre-orders (as of 2022). The assembly line takes 3 minutes to cook a pizza.
Zume Pizza Was One of the First Foodservice Robotics Start-Ups, it Failed
Zume was a company that was at the forefront of this trend, developing pizza-making robots that could quickly and efficiently churn out pies. The company raised hundreds of millions of dollars in funding (including $375 million from Softbank) and was said to be valued at over $4 billion at one point. However, it ultimately struggled to find a sustainable business model and ended up pivoting to sustainable packaging. The story is often used as a cautionary tale for how not all robotic companies are investable or have the right strategy to succeed in gaining accounts.
The Autonomous Fast-Food Store from Hyper
Hyper is a hyper-automated restaurant robot, capable of cooking pizza, burgers, bowls, salads, and delivering boulangerie and ice cream. It can increase ROI by 4x over what a normal store would have. Hyper can make 50 pizzas per hour, has cold storage for dough, and two robotic arms.
Pazzi Robotics Wants to Be the Future of Fast Food
Pazzi is a restaurant-in-a box concept, an autonomous restaurant that shows how the food is cooked. All the guest has to do is order and collect their meal. Pazzi uses machine learning to perform tasks without human intervention, able to make 10 pizzas simultaneously.
Stellar Pizza is Building Automated Pizza Trucks
Stellar Pizza builds automated pizza trucks launching in California in the autumn of 2022. The company estimates the labor costs savings in 16-20% range. As of mid 2022, the company has raised $9 million in total funding.
Smart Restaurant Kiosks and Vending Machines
Blendid Robotic Kiosks Are Producing Smoothies
Blendid produces automated food kiosks. The company has contracts with more than 500 foodservice companies such as Jamba, Walmart, Sodexo, and Love’s Travel Stops. Focus Brands, the parent company to Jamba invested in the startup. Blendid estimates a serviceable market of $15b-$20b and it’s focused on QSR. The kiosks cost between $100k-$125k and a service fee of around 20%.
Automated Retail Technologies Produces Intelligent Kiosks
The Florida-based company was founded in 2020 and already has a robotic kiosk (Reis & Irvy’s) that produces frozen treats and has also launched Just Baked Smart Bistros for fresh oven-baked foods. The food is produced in one minute and can be ordered at the kiosk or via app.
The BreadBot
The BreadBot automates bread making from mixing ingredients to baking and cooling the loaf. It produces up to 10 loaves per hour, which the company estimates to be the optimal number for a grocery store. Some estimates put the cost of a Breadbot at $100k paid over five years.
Cupcake Vending Machine
Already back in 2016 Sprinkles had Cupcakes ATMs across several locations. Each ATM could hold between 400 and 800 boxes with individual cupcakes (that are pre-made).
Coffee Robots Are Starting to Make Their Way into Coffee Shops
CafeX is a Robotic Coffee Bar
CafeX is a self-contained robotic bar that costs $230k plus a monthly fee of $1k for support. Customers place orders from a tablet, and the robot can produce 300-400 daily orders.
Rozum Robotics Has a Robot Barista
Rozum sells a robotic arm that works as a barista as well as a self-contained customizable kiosk (Rozum Café) where the robot can brew coffee in less than 3 minutes with an ROI of under 9 months. Rozum is also supplying Cubo Coffee House in Saudi Arabia, a robotic franchise.
Artly, a Barista Bot
Artly is a robotic barista that uses deep learning visual inspection to monitor drink quality. As of 2022, the company has five locations in California, Washington, and Oregon.
Truebird Are Fully Automated Self-Contained Coffee Kiosks
These micro-cafes are launching in 2022 in the NYC area. The company is backed by Torch Capital and Fantail Ventures, among others, and has raised $6.6m in four funding rounds.
Miso Robotics Also Has a Coffee Robot
The CookRight Coffee Robot is an AI-powered system that saves human monitoring time by tracking metrics such as volume, temperature, and time. Panera Bread is testing the system.
Switzerland-Based Barney Barista Can Serve Drinks and Coffee
Barney Barista is a robotic arm that can serve coffee as well as soft drinks, beer, and mocktails.
Ella, the Robot Barista
Ella is a creation of Crown Digital. The robotic arm can brew 300 coffee combinations and 200 cups per hour.
Henn na Café
This Japan-based robot café has customers placing orders at a vending machine and scanning a ticket for the robotic barista to prepare the beverage.
Monty Café Automates the Coffee Business in Russia and the UAE
Monty is a self-contained robotic coffee kiosk. The company offers the robotic coffee maker for free for those with airport contracts. There is no lump-sum payment, instead a 5% royalty fee is charged.
We Help Accelerate the Future of Foodservice
Restaurant Robots in Foodservice Chains
Several chains are starting to bet on robotics and automation through R&D, corporate venture capital, or running pilots and tests with foodservice technology companies. These are some of the restaurant chains betting on robotics.
Kitchen United Piloted Kiwibot
The kiwibot is an autonomous delivery vehicle that has been tested by ghost kitchen Kitchen United.
Domino’s Pizza Has Been Testing Nuro for Three Years
Domino’s started a partnership with last-mile autonomous delivery robot Nuro back in 2019. Nuro is being tested in Houston.
800 Degrees Partnering with Piestro
The fast-casual pizza chain has announced plans to deploy more than 3,500 pizza robots over the next five years.
Costco Is Using Automation to Put the Sauce in its Pizza
Costco uses a robot for the application of sauces in perfect conditions to maintain the quality of the product. It has the ability to produce 350 pizzas per hour.
Royal Caribbean Has Robotic Arms Prepping Cocktails
Royal Caribbean has been employing Makr Shakr in its Bionic Bar since 2016.
WhiteCastle Piloting Restaurant Robot Flippy
WhiteCastle was one of the first high-profile pilots for Miso Robotics hamburger flipper robot. After less than six months of piloting the robot at a Chicago location, the burger chain announced the robot will be in 100 of its restaurants by the end of 2022.
Chipotle Invested in Self-Driving Vehicle Nuro and is Testing Miso Robotics Flippy
Chipotle is giving a number of signals of its belief in the future of robots in restaurants.
In 2021 it invested in Nuro, an autonomous delivery company that could be used for last-mile food delivery. Nuro has been also backed by SoftBank and T. Rowe Price Associates.
In early 2022 Chipotle also partnered with Miso so that the robotic arm could help the back-of-house by frying tortilla chips.
And by mid-2022 it announced the investment (via its CVC arm) in Hyphen, an automated assembly line that can produce 350 meals per hour.
Buffalo Wild Wings is Also Testing Robots for Restaurants
Flippy is not the only restaurant robot out there but it’s certainly the most famous one. Part of that comes from getting high-profile pilots. BWW is testing Flippy to fry its wings.
Denny’s Tested a Restaurant Robot Server
Breakfast chain Denny’s tested robot servers to dispense orders back in 2021. The robot was named Janet.
Big Band Pizza in Atlanta is Employing Pepper
A pizzeria in Atlanta employs Pepper robot hostess to great people and robot Amy to serve the food.
Pizza HQ Using Robotics to Automate the Pizza-Making Process
Pizza HQ is a pizzeria using an automated pizza production line with a capacity of 500-1,500 pies per day, located in New Jersey. It opened in 2022 and it’s using Picnic robots.
Capprioti’s is Testing Piestro
The sandwich shop is piloting automated pizza ovens in up to 100 stores, starting with a location in Las Vegas.
Jamba Is Using Smoothie-Making Robots
Jamba Juice partnered with Blendid, a robotic arm with AI that prepares up to nine fresh smoothies at a time. The company is planning to deploy these robots in Love’s Travel Stops, to give access to travelers, and already has the Blendid kiosks in some universities.
Wow Bao Is Supplying Food Deserts With Vending Machines
The Asian fast-casual foodservice chain partnered with Automated Retail Technologies to pilot 50 vending machines in Florida and Georgia. The locations chosen are hospitals, airports, and hotels. The menu is bao and dumplings.
The Middle East is Also Adopting Robotics
Even markets with historically low labor costs, like the Middle East, are seeing the benefits of incorporating robotics to restaurants. Americana Group, a master franchisee with more than 2k restaurants is piloting Miso Robotics in one of their brands, Wimpy, at the Dubai Mall.
Costa Coffee is Innovating With Robot Kiosks
In 2020, Briggo’s Coffee Haus was acquired by Costa Coffee and re-branded as Costa Coffee BaristaBot.
If you are a robotics or automation company looking to grow into the foodservice industry, we can help.
The Benefits of Using Robots in Restaurants
Some of the advantages of using robots in restaurants are:
- More accurate than humans, fewer recipe mistakes
- Consistent quality
- Reduce food waste
- Employ less labor
- Improve throughput and speed
- Better safety and sanitation
- Works 24×7 without taking breaks
- Analytics allow for improving efficiency and food quality
- Can free humans from jobs that are boring and repetitive
There are many robotic companies and not all of them are investable. If you are an investor looking to do due diligence on a foodservice technology company, or seeking an accurate evaluation of the foodservice tech ecosystem, or support with your investment thesis, we can help.
The Challenges of Implementing Robotics in Restaurants
While automation can help reduce labor costs, it is not yet a straightforward application to restaurant kitchens and front-of-house. Because of the myriad of activities in the kitchen (and in restaurants in general), robots need to be specifically designed to be able to handle a variety of tasks, from frying to seasoning to preparing drinks to taking orders from guests. Additionally, robots can’t adapt to changing situations and are really bad at reading human emotions, which means they still have to work under human supervision.
Restaurant robots are still costly, and though most companies are starting to make accurate risk-benefit calculations (based on labor savings and opportunity costs), they remain out of the budget for most independent restaurants.
The Restaurant of The Future Is Closer Than You Think
Even though robotics is still not a significant piece of the foodservice industry yet, it is starting to mature. After the COVID-19 pandemic and with factors such as increasing labor costs and SaaS allowing to lower the initial investment, we can expect restaurant robotics to boom over the next few years.
The largest employer in the world of restaurants will no longer be McDonald’s, it will be companies that control the robots. It’s happening much faster than most people realize.
Robots could take those tasks that are boring, dangerous, and time-consuming so that people don’t have to do them. However, as of 2022 we estimate robots wages (measured by SaaS payments) do not exceed $10 million globally.
Robots can help with back-of-house and front-of-house. Back-of-house: handling fryers, flipping burgers or steaks, cleaning, prepping ingredients, preparing drinks, and more. Front-of-house: greeting guests, taking orders, delivering food to the table.
Several restaurant chains have piloted robots on their premises. Some of the most high-profile ones are WhiteCastle, Chipotle, Domino’s, Buffalo Wild Wings, Royal Caribbean cruises, and Kitchen United (ghost kitchens).
There are many restaurant robot companies. Some are: Nala, Miso, Picnic, Cecilia.ai, Piestro, and Makr Shakr.
The cost of restaurant robots can start at around $1,500-$3,000 monthly. Most companies charge an initial installation fee as well that could range in the $20,000-$30,000.
About Aaron Allen & Associates
Aaron Allen & Associates is a global restaurant consultancy specializing in brand strategy, growth and expansion, and value enhancement. We have worked with a wide range of clients including multibillion-dollar chains, hotels, manufacturers, associations, and prestigious private equity firms.
We help clients imagine, articulate, and realize a compelling vision of the future, align and cascade resources, and engage and enroll shareholders and stakeholders alike to develop multi-year roadmaps that bridge the gap between current-state conditions and future-state ambitions. Learn More.
